Mapping Applications of Computer Simulation in Orthopaedic Services: A Topic Modeling Approach
The paper “Mapping Applications of Computer Simulation in Orthopedic Services: A Topic Modeling Approach” has been submitted to the Winter Simulation Conference, 2025 (Seattle) under the Health & Life Sciences Track.
Orthopaedic health services are characterised by high patient volumes, long elective waits, unpredictable emergency demand, and close coupling with other hospital processes. These present significant challenges for meeting operational targets and maintaining quality of care. In healthcare, simulation has been widely used for addressing such challenges. Topic modelling is used to identify and analyse academic papers using simulation to address operational-level challenges for orthopaedic service delivery. We analyzed 37 papers over twenty years, combining a structured analysis with topic modelling to categorize and map applications. Despite widespread recognition of its potential, simulation remains underutilised in orthopaedics, with fragmented application and limited real-world implementation. Recent trends indicate a shift toward system-wide approaches that better align with operational realities and stakeholder needs. Future research should aim to bridge methodological innovation with collaboration and practical application, such as hybrid and real-time simulation approaches focusing on stakeholder needs, and integrating relevant operational performance metrics.
The study aims to investigate how simulation has been used to support operational-level service planning in trauma and orthopedic services. The purpose of the study is to understand the current state-of-the-art, and to identify research gaps and opportunities to strengthen the implementation of simulation for orthopedic service planning. The specific aims are:
To identify studies that have used simulation methods for evaluating orthopedic service delivery;
To investigate methods, application areas, context of care, key performance indicators, and outcomes;
To classify papers by topics, and map the application domain focusing on future opportunities.
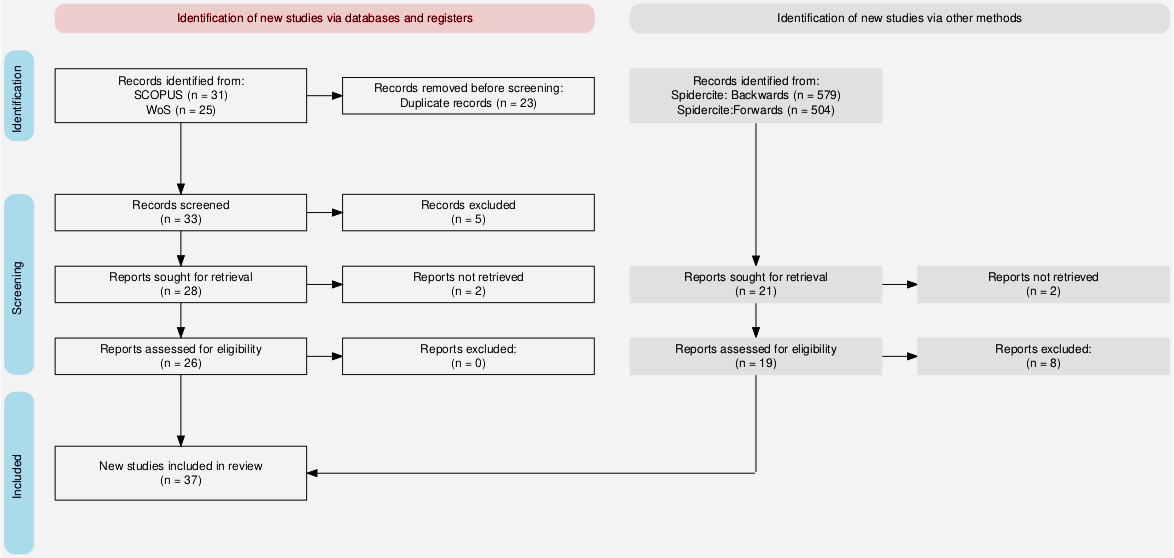
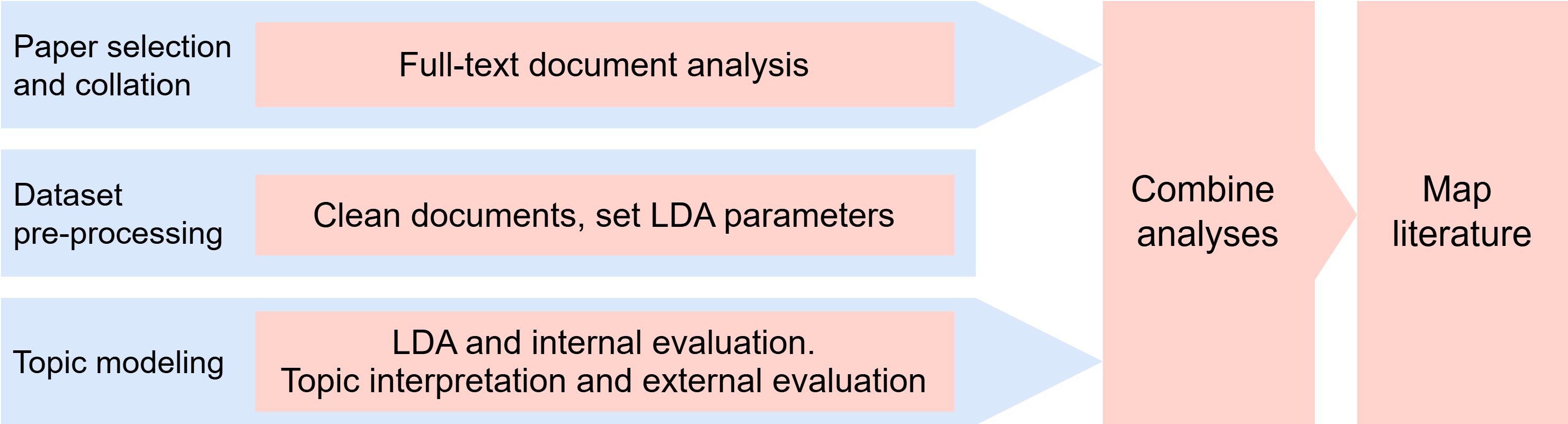
We use a structured full-text analysis combined with topic modeling to analyze and synthesize the literature. Topic modeling is an unsupervised machine learning technique that identifies underlying themes or topics in large text datasets by grouping related words and concepts. It was conducted to supplement the structured analysis by revealing latent themes and relationships within the literature. Examining relationships between topics and the structured analysis can help identify emerging trends and gaps in the existing body of knowledge. Given the small size of our dataset, the structured analysis enhances topic coherence and interpretability, while topic modeling adds a systematic and reproducible layer of abstraction that uncovers patterns and relationships in the literature with greater rigor than manual review alone. Topic modelling was performed using Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA), implemented via Gibbs sampling in R v4.4.2.
Check out the repository
to see our search strings, inclusion/exclusion criteria, and all data and analysis for this paper.

Back to top




